| Electromagnetism |
|
|
|
Electrostatics
- Electric charge
- Static electricity
- Insulator
- Triboelectricity
- Electrostatic discharge
- Induction
- Coulomb's law
- Gauss's law
- Electric flux / potential energy
|
Magnetostatics
- Ampère's law
- Magnetic field
- Magnetization
- Magnetic flux
- Gauss's law for magnetism
|
Electrodynamics
- Electromagnetic induction
- Lenz's law
- Displacement current
- Electromagnetic radiation
- Maxwell tensor
- Poynting vector
- Liénard–Wiechert potential
|
Electrical network
- Electric current
- Electric potential
- Series circuit
- Parallel circuit
- Direct current
- Alternating current
- Charged current
- Neutral current
- Electromotive force
- Capacitance
- Resonant cavities
- Waveguides
|
Covariant formulation
Electromagnetic tensor
(stress–energy tensor)
- Electromagnetic four-potential
|
Scientists
- Ampère
- Coulomb
- Faraday
- Gauss
- Heaviside
- Henry
- Hertz
- Lorentz
- Maxwell
- Tesla
- Volta
- Weber
- Ørsted
|
|
|
Coulomb's law or Coulomb's inverse-square law, is a law of physics that describes force interacting between static electrically charged particles. In its scalar form the law is:
- ,
where ke is Coulomb's constant (ke = 7009899000000000000♠8.99×109 N m2 C−2), q1 and q2 are the signed magnitudes of the charges, the scalar r is the distance between the charges. The force of interaction between the charges is attractive if the charges are opposite signed and repulsive if like signed.
The law was first published in 1784 by French physicist Charles Augustin de Coulomb and was essential to the development of the theory of electromagnetism. It is analogous to Isaac Newton's inverse-square law of universal gravitation. Coulomb's law can be used to derive Gauss's law, and vice versa. The law has been tested heavily, and all observations have upheld the law's principle.
Contents
- 1 The law
- 1.1 Units
- 1.2 Electric field
- 1.3 Coulomb's constant
- 1.4 Conditions for validity
- 2 Scalar form
- 3 Vector form
- 3.1 System of discrete charges
- 3.2 Continuous charge distribution
- 4 Simple experiment to verify Coulomb's law
- 5 Electrostatic approximation
- 6 See also
- 7 Notes
- 8 References
- 9 External links
The law
Coulomb's law states that:
The magnitude of the electrostatic force of interaction between two point charges is directly proportional to the scalar multiplication of the magnitudes of charges and inversely proportional to the square of the distance between them.[1]
The force is along the straight line joining them. If the two charges have the same sign, the electrostatic force between them is repulsive; if they have different signs, the force between them is attractive.
Coulomb's law can also be stated as a simple mathematical expression. The scalar and vector forms of the mathematical equation are
- and respectively,
where ke is Coulomb's constant (ke = 7009898755178736817♠8.9875517873681764×109 N m2 C−2), q1 and q2 are the signed magnitudes of the charges, the scalar r is the distance between the charges, the vector r21 = r1 − r2 is the vectorial distance between the charges, and r̂21 = r21/|r21| (a unit vector pointing from q2 to q1). The vector form of the equation calculates the force F1 applied on q1 by q2. If r12 is used instead, then the effect on q2 can be found. It can be also calculated using Newton's third law: F2 = −F1.
Units
Electromagnetic theory is usually expressed using the standard SI units. Force is measured in newtons, charge in coulombs, and distance in metres. Coulomb's constant is given by ke = 1/4πε0. The constant ε0 is the permittivity of free space in C2 m−2 N−1. And ε is the relative permittivity of the material in which the charges are immersed, and is dimensionless.
The SI derived units for the electric field are volts per meter, newtons per coulomb, or tesla meters per second.
Coulomb's law and Coulomb's constant can also be interpreted in various terms:
- Atomic units. In atomic units the force is expressed in hartrees per Bohr radius, the charge in terms of the elementary charge, and the distances in terms of the Bohr radius.
- Electrostatic units or Gaussian units. In electrostatic units and Gaussian units, the unit charge (esu or statcoulomb) is defined in such a way that the Coulomb constant k disappears because it has the value of one and becomes dimensionless.
Electric field
If the two charges have the same sign, the electrostatic force between them is repulsive; if they have different sign, the force between them is attractive.
An electric field is a vector field that associates to each point in space the Coulomb force experienced by a test charge. In the simplest case, the field is considered to be generated solely by a single source point charge. The strength and direction of the Coulomb force F on a test charge qt depends on the electric field E that it finds itself in, such that F = qtE. If the field is generated by a positive source point charge q, the direction of the electric field points along lines directed radially outwards from it, i.e. in the direction that a positive point test charge qt would move if placed in the field. For a negative point source charge, the direction is radially inwards.
The magnitude of the electric field E can be derived from Coulomb's law. By choosing one of the point charges to be the source, and the other to be the test charge, it follows from Coulomb's law that the magnitude of the electric field E created by a single source point charge q at a certain distance from it r in vacuum is given by:
Coulomb's constant
Main article: Coulomb's constant
Coulomb's constant is a proportionality factor that appears in Coulomb's law as well as in other electric-related formulas. Denoted ke, it is also called the electric force constant or electrostatic constant, hence the subscript e.
The exact value of Coulomb's constant is:

Conditions for validity
There are two conditions to be fulfilled for the validity of Coulomb’s law:
- The charges considered must be point charges.
- They should be stationary with respect to each other.
Scalar form
The absolute value of the force
F between two point charges
q and
Q relates to the distance between the point charges and to the simple product of their charges. The diagram shows that like charges repel each other, and opposite charges attract each other.
When it is only of interest to know the magnitude of the electrostatic force (and not its direction), it may be easiest to consider a scalar version of the law. The scalar form of Coulomb's Law relates the magnitude and sign of the electrostatic force F acting simultaneously on two point charges q1 and q2 as follows:
where r is the separation distance and ke is Coulomb's constant. If the product q1q2 is positive, the force between the two charges is repulsive; if the product is negative, the force between them is attractive.[2]
Vector form
In the image, the vector
F1 is the force experienced by
q1, and the vector
F2 is the force experienced by
q2. When
q1q2 > 0 the forces are repulsive (as in the image) and when q1q2 < 0 the forces are attractive (opposite to the image). The magnitude of the forces will always be equal.
Coulomb's law states that the electrostatic force F1 experienced by a charge, q1 at position r1, in the vicinity of another charge, q2 at position r2, in a vacuum is equal to:
where r21 = r1 − r2, the unit vector r̂21 = r21/|r21|, and ε0 is the electric constant.
The vector form of Coulomb's law is simply the scalar definition of the law with the direction given by the unit vector, r̂21, parallel with the line from charge q2 to charge q1.[3] If both charges have the same sign (like charges) then the product q1q2 is positive and the direction of the force on q1 is given by r̂21; the charges repel each other. If the charges have opposite signs then the product q1q2 is negative and the direction of the force on q1 is given by −r̂21 = r̂12; the charges attract each other.
The electrostatic force F2 experienced by q2, according to Newton's third law, is F2 = −F1.
System of discrete charges
The law of superposition allows Coulomb's law to be extended to include any number of point charges. The force acting on a point charge due to a system of point charges is simply the vector addition of the individual forces acting alone on that point charge due to each one of the charges. The resulting force vector is parallel to the electric field vector at that point, with that point charge removed.
The force F on a small charge q at position r, due to a system of N discrete charges in vacuum is:
where qi and ri are the magnitude and position respectively of the ith charge, R̂i is a unit vector in the direction of Ri = r − ri (a vector pointing from charges qi to q).[3]
Continuous charge distribution
In this case, the principle of linear superposition is also used. For a continuous charge distribution, an integral over the region containing the charge is equivalent to an infinite summation, treating each infinitesimal element of space as a point charge dq. The distribution of charge is usually linear, surface or volumetric.
For a linear charge distribution (a good approximation for charge in a wire) where λ(r′) gives the charge per unit length at position r′, and dl′ is an infinitesimal element of length,
- .[4]
For a surface charge distribution (a good approximation for charge on a plate in a parallel plate capacitor) where σ(r′) gives the charge per unit area at position r′, and dA′ is an infinitesimal element of area,
For a volume charge distribution (such as charge within a bulk metal) where ρ(r′) gives the charge per unit volume at position r′, and dV′ is an infinitesimal element of volume,
- [3]
The force on a small test charge q′ at position r in vacuum is given by the integral over the distribution of charge:
Simple experiment to verify Coulomb's law
Experiment to verify Coulomb's law.
It is possible to verify Coulomb's law with a simple experiment. Consider two small spheres of mass m and same-sign charge q, hanging from two ropes of negligible mass of length l. The forces acting on each sphere are three: the weight mg, the rope tension T and the electric force F.
In the equilibrium state:
and:
Dividing (1) by (2):
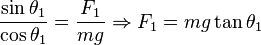
|
|
(3)
|
Let L1 be the distance between the charged spheres; the repulsion force between them F1, assuming Coulomb's law is correct, is equal to
so:
If we now discharge one of the spheres, and we put it in contact with the charged sphere, each one of them acquires a charge q/2. In the equilibrium state, the distance between the charges will be L2 < L1 and the repulsion force between them will be:
We know that F2 = mg tan θ2. And:
Dividing (4) by (5), we get:

|
|
(6)
|
Measuring the angles θ1 and θ2 and the distance between the charges L1 and L2 is sufficient to verify that the equality is true taking into account the experimental error. In practice, angles can be difficult to measure, so if the length of the ropes is sufficiently great, the angles will be small enough to make the following approximation:
Using this approximation, the relationship (6) becomes the much simpler expression:
In this way, the verification is limited to measuring the distance between the charges and check that the division approximates the theoretical value.
Electrostatic approximation
In either formulation, Coulomb’s law is fully accurate only when the objects are stationary, and remains approximately correct only for slow movement. These conditions are collectively known as the electrostatic approximation. When movement takes place, magnetic fields that alter the force on the two objects are produced. The magnetic interaction between moving charges may be thought of as a manifestation of the force from the electrostatic field but with Einstein’s theory of relativity taken into consideration.
Atomic forces
Coulomb's law holds even within atoms, correctly describing the force between the positively charged atomic nucleus and each of the negatively charged electrons. This simple law also correctly accounts for the forces that bind atoms together to form molecules and for the forces that bind atoms and molecules together to form solids and liquids. Generally, as the distance between ions increases, the energy of attraction approaches zero and ionic bonding is less favorable. As the magnitude of opposing charges increases, energy increases and ionic bonding is more favorable.
See also
- Biot–Savart law
- Darwin Lagrangian
- Electromagnetic force
- Gauss's law
- Method of image charges
- Molecular modelling
- Newton's law of universal gravitation, which uses a similar structure, but for mass instead of charge
- Static forces and virtual-particle exchange
Notes
- ^ Coulomb (1785a) "Premier mémoire sur l’électricité et le magnétisme," Histoire de l’Académie Royale des Sciences, pages 569-577 — Coulomb studied the repulsive force between bodies having electrical charges of the same sign:
Il résulte donc de ces trois essais, que l'action répulsive que les deux balles électrifées de la même nature d'électricité exercent l'une sur l'autre, suit la raison inverse du carré des distances.
Translation: It follows therefore from these three tests, that the repulsive force that the two balls — [that were] electrified with the same kind of electricity — exert on each other, follows the inverse proportion of the square of the distance.
Coulomb also showed that oppositely charged bodies obey an inverse-square law of attraction.
- ^ Coulomb's law, Hyperphysics
- ^ a b c Coulomb's law, University of Texas
- ^ Charged rods, PhysicsLab.org
References
- Coulomb, Charles Augustin (1788) [1785]. "Premier mémoire sur l’électricité et le magnétisme". Histoire de l’Académie Royale des Sciences. Imprimerie Royale. pp. 569–577.
- Coulomb, Charles Augustin (1788) [1785]. "Second mémoire sur l’électricité et le magnétisme". Histoire de l’Académie Royale des Sciences. Imprimerie Royale. pp. 578–611.
- Griffiths, David J. (1998). Introduction to Electrodynamics (3rd ed.). Prentice Hall. ISBN 0-13-805326-X.
- Tipler, Paul A.; Mosca, Gene (2008). Physics for Scientists and Engineers (6th ed.). New York: W. H. Freeman and Company. ISBN 0-7167-8964-7. LCCN 2007010418.
- Young, Hugh D.; Freedman, Roger A. (2010). Sears and Zemansky's University Physics : With Modern Physics (13th ed.). Addison-Wesley (Pearson). ISBN 978-0-321-69686-1.
External links
- Coulomb's Law on Project PHYSNET
- Electricity and the Atom—a chapter from an online textbook
- A maze game for teaching Coulomb's Law—a game created by the Molecular Workbench software
- Electric Charges, Polarization, Electric Force, Coulomb's Law Walter Lewin, 8.02 Electricity and Magnetism, Spring 2002: Lecture 1 (video). MIT OpenCourseWare. License: Creative Commons Attribution-Noncommercial-Share Alike.