WordNet
- (medicine) the invasion of the body by pathogenic microorganisms and their multiplication which can lead to tissue damage and disease
- (phonetics) the alteration of a speech sound under the influence of a neighboring sound
- the pathological state resulting from the invasion of the body by pathogenic microorganisms
- (international law) illegality that taints or contaminates a ship or cargo rendering it liable to seizure
- moral corruption or contamination; "ambitious men are led astray by an infection that is almost unavoidable"
- an incident in which an infectious disease is transmitted (同)contagion, transmission
- a sexually transmitted infection caused by bacteria of the genus Chlamydia
- coccoid rickettsia infesting birds and mammals; cause infections of eyes and lungs and genitourinary tract
PrepTutorEJDIC
- 〈U〉(病気の)伝染;感染 / 〈C〉伝染病
Wikipedia preview
出典(authority):フリー百科事典『ウィキペディア(Wikipedia)』「2022/11/30 08:12:21」(JST)
wiki en
| Chlamydia | |
|---|---|
| Other names | Chlamydia infection |
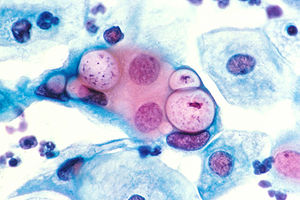 | |
| Pap smear showing C. trachomatis (H&E stain) | |
| Pronunciation |
|
| Specialty | Infectious disease, gynecology, urology |
| Symptoms | None, vaginal discharge, discharge from the penis, burning with urination[1] |
| Complications | Pain in the testicles, pelvic inflammatory disease, infertility, ectopic pregnancy[1][2] |
| Usual onset | Few weeks following exposure[1] |
| Causes | Chlamydia trachomatis spread by sexual intercourse or childbirth[3] |
| Diagnostic method | Urine or swab of the cervix, vagina, or urethra[2] |
| Prevention | Not having sex, condoms, sex with only one non–infected person[1] |
| Treatment | Antibiotics (azithromycin or doxycycline)[2] |
| Frequency | 4.2% (women), 2.7% (men)[4][5] |
| Deaths | ~200 (2015)[6] |
Chlamydia, or more specifically a chlamydia infection, is a sexually transmitted infection caused by the bacterium Chlamydia trachomatis.[3] Most people who are infected have no symptoms.[1] When symptoms do appear they may occur only several weeks after infection;[1] the incubation period between exposure and being able to infect others is thought to be on the order of two to six weeks.[7] Symptoms in women may include vaginal discharge or burning with urination.[1] Symptoms in men may include discharge from the penis, burning with urination, or pain and swelling of one or both testicles.[1] The infection can spread to the upper genital tract in women, causing pelvic inflammatory disease, which may result in future infertility or ectopic pregnancy.[2]
Chlamydia infections can occur in other areas besides the genitals, including the anus, eyes, throat, and lymph nodes. Repeated chlamydia infections of the eyes that go without treatment can result in trachoma, a common cause of blindness in the developing world.[8]
Chlamydia can be spread during vaginal, anal, or oral sex, and can be passed from an infected mother to her baby during childbirth.[1] The eye infections may also be spread by personal contact, flies, and contaminated towels in areas with poor sanitation.[8] Infection by the bacterium Chlamydia trachomatis only occurs in humans.[9] Diagnosis is often by screening which is recommended yearly in sexually active women under the age of twenty-five, others at higher risk, and at the first prenatal visit.[1][2] Testing can be done on the urine or a swab of the cervix, vagina, or urethra.[2] Rectal or mouth swabs are required to diagnose infections in those areas.[2]
Prevention is by not having sex, the use of condoms, or having sex with only one other person, who is not infected.[1] Chlamydia can be cured by antibiotics with typically either azithromycin or doxycycline being used.[2] Erythromycin or azithromycin is recommended in babies and during pregnancy.[2] Sexual partners should also be treated, and infected people should be advised not to have sex for seven days and until symptom free.[2] Gonorrhea, syphilis, and HIV should be tested for in those who have been infected.[2] Following treatment people should be tested again after three months.[2]
Chlamydia is one of the most common sexually transmitted infections, affecting about 4.2% of women and 2.7% of men worldwide.[4][5] In 2015, about 61 million new cases occurred globally.[10] In the United States about 1.4 million cases were reported in 2014.[3] Infections are most common among those between the ages of 15 and 25 and are more common in women than men.[2][3] In 2015 infections resulted in about 200 deaths.[6] The word chlamydia is from the Greek χλαμύδα, meaning "cloak".[11][12]
Contents
- 1 Signs and symptoms
- 1.1 Genital disease
- 1.1.1 Women
- 1.1.2 Men
- 1.2 Eye disease
- 1.3 Joints
- 1.4 Infants
- 1.5 Other conditions
- 1.1 Genital disease
- 2 Transmission
- 3 Pathophysiology
- 4 Diagnosis
- 5 Prevention
- 5.1 Screening
- 6 Treatment
- 7 Epidemiology
- 8 References
- 9 External links
Signs and symptoms
Genital disease


Women
Chlamydial infection of the cervix (neck of the womb) is a sexually transmitted infection which has no symptoms for around 70% of women infected. The infection can be passed through vaginal, anal, or oral sex. Of those who have an asymptomatic infection that is not detected by their doctor, approximately half will develop pelvic inflammatory disease (PID), a generic term for infection of the uterus, fallopian tubes, and/or ovaries. PID can cause scarring inside the reproductive organs, which can later cause serious complications, including chronic pelvic pain, difficulty becoming pregnant, ectopic (tubal) pregnancy, and other dangerous complications of pregnancy.[13] Chlamydia is known as the "silent epidemic", as at least 70% of genital C. trachomatis infections in women (and 50% in men) are asymptomatic at the time of diagnosis,[14] and can linger for months or years before being discovered. Signs and symptoms may include abnormal vaginal bleeding or discharge, abdominal pain, painful sexual intercourse, fever, painful urination or the urge to urinate more often than usual (urinary urgency).[13] For sexually active women who are not pregnant, screening is recommended in those under 25 and others at risk of infection.[15] Risk factors include a history of chlamydial or other sexually transmitted infection, new or multiple sexual partners, and inconsistent condom use.[16] Guidelines recommend all women attending for emergency contraceptive are offered chlamydia testing, with studies showing up to 9% of women aged <25 years had chlamydia.[17]
Men
In men, those with a chlamydial infection show symptoms of infectious inflammation of the urethra in about 50% of cases.[14] Symptoms that may occur include: a painful or burning sensation when urinating, an unusual discharge from the penis, testicular pain or swelling, or fever. If left untreated, chlamydia in men can spread to the testicles causing epididymitis, which in rare cases can lead to sterility if not treated.[14] Chlamydia is also a potential cause of prostatic inflammation in men, although the exact relevance in prostatitis is difficult to ascertain due to possible contamination from urethritis.[18]
Eye disease

Trachoma is a chronic conjunctivitis caused by Chlamydia trachomatis.[19] It was once the leading cause of blindness worldwide, but its role diminished from 15% of blindness cases by trachoma in 1995 to 3.6% in 2002.[20][21] The infection can be spread from eye to eye by fingers, shared towels or cloths, coughing and sneezing and eye-seeking flies.[22] Symptoms include mucopurulent ocular discharge, irritation, redness, and lid swelling.[19] Newborns can also develop chlamydia eye infection through childbirth (see below). Using the SAFE strategy (acronym for surgery for in-growing or in-turned lashes, antibiotics, facial cleanliness, and environmental improvements), the World Health Organization aims for the global elimination of trachoma by 2020 (GET 2020 initiative).[23][24]
Joints
Chlamydia may also cause reactive arthritis—the triad of arthritis, conjunctivitis and urethral inflammation—especially in young men. About 15,000 men develop reactive arthritis due to chlamydia infection each year in the U.S., and about 5,000 are permanently affected by it. It can occur in both sexes, though is more common in men.[citation needed]
Infants
As many as half of all infants born to mothers with chlamydia will be born with the disease. Chlamydia can affect infants by causing spontaneous abortion; premature birth; conjunctivitis, which may lead to blindness; and pneumonia.[25] Conjunctivitis due to chlamydia typically occurs one week after birth (compared with chemical causes (within hours) or gonorrhea (2–5 days)).[citation needed]
Other conditions
A different serovar of Chlamydia trachomatis is also the cause of lymphogranuloma venereum, an infection of the lymph nodes and lymphatics. It usually presents with genital ulceration and swollen lymph nodes in the groin, but it may also manifest as rectal inflammation, fever or swollen lymph nodes in other regions of the body.[26]
Transmission
Chlamydia can be transmitted during vaginal, anal, or oral sex, or direct contact with infected tissue such as conjunctiva. Chlamydia can also be passed from an infected mother to her baby during vaginal childbirth.[25] It is assumed that the probability of becoming infected is proportionate to the number of bacteria one is exposed to.[27]
Pathophysiology
Chlamydiae have the ability to establish long-term associations with host cells. When an infected host cell is starved for various nutrients such as amino acids (for example, tryptophan),[28] iron, or vitamins, this has a negative consequence for Chlamydiae since the organism is dependent on the host cell for these nutrients. Long-term cohort studies indicate that approximately 50% of those infected clear within a year, 80% within two years, and 90% within three years.[29]
The starved chlamydiae enter a persistent growth state wherein they stop cell division and become morphologically aberrant by increasing in size.[30] Persistent organisms remain viable as they are capable of returning to a normal growth state once conditions in the host cell improve.[citation needed]
There is debate as to whether persistence has relevance. Some believe that persistent chlamydiae are the cause of chronic chlamydial diseases. Some antibiotics such as β-lactams have been found to induce a persistent-like growth state.[31][32]
Diagnosis

The diagnosis of genital chlamydial infections evolved rapidly from the 1990s through 2006. Nucleic acid amplification tests (NAAT), such as polymerase chain reaction (PCR), transcription mediated amplification (TMA), and the DNA strand displacement amplification (SDA) now are the mainstays. NAAT for chlamydia may be performed on swab specimens sampled from the cervix (women) or urethra (men), on self-collected vaginal swabs, or on voided urine.[33] NAAT has been estimated to have a sensitivity of approximately 90% and a specificity of approximately 99%, regardless of sampling from a cervical swab or by urine specimen.[34] In women seeking an sexually transmitted infection (STI) clinic and a urine test is negative, a subsequent cervical swab has been estimated to be positive in approximately 2% of the time.[34]
At present, the NAATs have regulatory approval only for testing urogenital specimens, although rapidly evolving research indicates that they may give reliable results on rectal specimens.
Because of improved test accuracy, ease of specimen management, convenience in specimen management, and ease of screening sexually active men and women, the NAATs have largely replaced culture, the historic gold standard for chlamydia diagnosis, and the non-amplified probe tests. The latter test is relatively insensitive, successfully detecting only 60–80% of infections in asymptomatic women, and often giving falsely-positive results. Culture remains useful in selected circumstances and is currently the only assay approved for testing non-genital specimens. Other methods also exist including: ligase chain reaction (LCR), direct fluorescent antibody resting, enzyme immunoassay, and cell culture.[35]
Rapid point-of-care tests are, as of 2020, not thought to be effective for diagnosing chlamydia in men of reproductive age and nonpregnant women because of high false-negative rates.[36]
Prevention
Prevention is by not having sex, the use of condoms, or having sex with only one other person, who is not infected.[1]
Screening
For sexually active women who are not pregnant, screening is recommended in those under 25 and others at risk of infection.[15] Risk factors include a history of chlamydial or other sexually transmitted infection, new or multiple sexual partners, and inconsistent condom use.[16] For pregnant women, guidelines vary: screening women with age or other risk factors is recommended by the U.S. Preventive Services Task Force (USPSTF) (which recommends screening women under 25) and the American Academy of Family Physicians (which recommends screening women aged 25 or younger). The American College of Obstetricians and Gynecologists recommends screening all at risk, while the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention recommend universal screening of pregnant women.[15] The USPSTF acknowledges that in some communities there may be other risk factors for infection, such as ethnicity.[15] Evidence-based recommendations for screening initiation, intervals and termination are currently not possible.[15] For men, the USPSTF concludes evidence is currently insufficient to determine if regular screening of men for chlamydia is beneficial.[16] They recommend regular screening of men who are at increased risk for HIV or syphilis infection.[16] A Cochrane review found that the effects of screening are uncertain in terms of chlamydia transmission but that screening probably reduces the risk of pelvic inflammatory disease in women.[37]
In the United Kingdom the National Health Service (NHS) aims to:
- Prevent and control chlamydia infection through early detection and treatment of asymptomatic infection;
- Reduce onward transmission to sexual partners;
- Prevent the consequences of untreated infection;
- Test at least 25 percent of the sexually active under 25 population annually.[38]
- Retest after treatment.[39]
Treatment
C. trachomatis infection can be effectively cured with antibiotics. Guidelines recommend azithromycin, doxycycline, erythromycin, levofloxacin or ofloxacin.[40] In men, doxycycline (100 mg twice a day for 7 days) is probably more effective than azithromycin (1 g single dose) but evidence for the relative effectiveness of antibiotics in women is very uncertain.[41] Agents recommended during pregnancy include erythromycin or amoxicillin.[2][42]
An option for treating sexual partners of those with chlamydia or gonorrhea includes patient-delivered partner therapy (PDT or PDPT), which is the practice of treating the sex partners of index cases by providing prescriptions or medications to the patient to take to his/her partner without the health care provider first examining the partner.[43]
Following treatment people should be tested again after three months to check for reinfection.[2]
Epidemiology
Globally, as of 2015, sexually transmitted chlamydia affects approximately 61 million people.[10] It is more common in women (3.8%) than men (2.5%).[45] In 2015 it resulted in about 200 deaths.[6]
In the United States about 1.6 million cases were reported in 2016.[46] The CDC estimates that if one includes unreported cases there are about 2.9 million each year.[46] It affects around 2% of young people.[47] Chlamydial infection is the most common bacterial sexually transmitted infection in the UK.[48]
Chlamydia causes more than 250,000 cases of epididymitis in the U.S. each year. Chlamydia causes 250,000 to 500,000 cases of PID every year in the United States. Women infected with chlamydia are up to five times more likely to become infected with HIV, if exposed.[25]
References
- ^ a b c d e f g h i j k l "Chlamydia – CDC Fact Sheet". CDC. May 19, 2016. Archived from the original on 11 June 2016. Retrieved 10 June 2016.
- ^ a b c d e f g h i j k l m n o "2015 Sexually Transmitted Diseases Treatment Guidelines". CDC. June 4, 2015. Archived from the original on 11 June 2016. Retrieved 10 June 2016.
- ^ a b c d "2014 Sexually Transmitted Diseases Surveillance Chlamydia". November 17, 2015. Archived from the original on 10 June 2016. Retrieved 10 June 2016.
- ^ a b Newman, Lori; Rowley, Jane; Vander Hoorn, Stephen; Wijesooriya, Nalinka Saman; Unemo, Magnus; Low, Nicola; Stevens, Gretchen; Gottlieb, Sami; Kiarie, James; Temmerman, Marleen; Meng, Zhefeng (8 December 2015). "Global Estimates of the Prevalence and Incidence of Four Curable Sexually Transmitted Infections in 2012 Based on Systematic Review and Global Reporting". PLOS ONE. 10 (12): e0143304. Bibcode:2015PLoSO..1043304N. doi:10.1371/journal.pone.0143304. PMC 4672879. PMID 26646541.
- ^ a b "Sexually transmitted infections (STIs) Fact sheet N°110". who.int. December 2015. Archived from the original on 25 November 2014. Retrieved 10 June 2016.
- ^ a b c GBD 2015 Mortality and Causes of Death, Collaborators. (8 October 2016). "Global, regional, and national life expectancy, all-cause mortality, and cause-specific mortality for 249 causes of death, 1980–2015: a systematic analysis for the Global Burden of Disease Study 2015". Lancet. 388 (10053): 1459–1544. doi:10.1016/s0140-6736(16)31012-1. PMC 5388903. PMID 27733281.
{{cite journal}}:|first1=has generic name (help) - ^ Teri Shors (2018). Krasner's Microbial Challenge. p. 366.
- ^ a b "CDC – Trachoma, Hygiene-related Diseases, Healthy Water". Centers for Disease Control and Prevention. December 28, 2009. Archived from the original on September 5, 2015. Retrieved 2015-07-24.
- ^ Graeter, Linda (2014). Elsevier's Medical Laboratory Science Examination Review. Elsevier Health Sciences. p. 30. ISBN 9780323292412. Archived from the original on 2017-09-10.
- ^ a b GBD 2015 Disease and Injury Incidence and Prevalence, Collaborators. (8 October 2016). "Global, regional, and national incidence, prevalence, and years lived with disability for 310 diseases and injuries, 1990–2015: a systematic analysis for the Global Burden of Disease Study 2015". Lancet. 388 (10053): 1545–1602. doi:10.1016/S0140-6736(16)31678-6. PMC 5055577. PMID 27733282.
{{cite journal}}:|first1=has generic name (help) - ^ Stevenson, Angus (2010). Oxford dictionary of English (3rd ed.). New York, NY: Oxford University Press. p. 306. ISBN 9780199571123. Archived from the original on 10 September 2017. Retrieved 10 June 2016.
- ^ Byrne, Gerald I. (8 July 2003). "uncloaked". Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences. 100 (14): 8040–8042. doi:10.1073/pnas.1533181100. PMC 166176. PMID 12835422.
The term was coined based on the incorrect conclusion that Chlamydia are intracellular protozoan pathogens that appear to cloak the nucleus of infected cells.
- ^ a b Witkin SS, Minis E, Athanasiou A, Leizer J, Linhares IM (October 2017). "Chlamydia trachomatis: the Persistent Pathogen". Clinical and Vaccine Immunology. 24 (10). doi:10.1128/CVI.00203-17. PMC 5629669. PMID 28835360.
- ^ a b c NHS Chlamydia page Archived 2013-01-16 at the Wayback Machine
- ^ a b c d e Meyers D, Wolff T, Gregory K, et al. (2008). "USPSTF Recommendations for STI Screening". Am Fam Physician. 77 (6): 819–824. PMID 18386598. Archived from the original on 2021-08-28. Retrieved 2008-03-17.
- ^ a b c d U.S. Preventive Services Task Force (2007). "Screening for chlamydial infection: U.S. Preventive Services Task Force recommendation statement". Ann Intern Med. 147 (2): 128–34. doi:10.7326/0003-4819-147-2-200707170-00172. PMID 17576996. Archived from the original on 2008-03-03.
- ^ Yeung E, Comben E, McGarry C, Warrington R (2015). "STI testing in emergency contraceptive consultations". British Journal of General Practice. 65 (631): 63–64. doi:10.3399/bjgp15X683449. PMC 4325454. PMID 25624285.
- ^ Wagenlehner FM, Naber KG, Weidner W (2006). "Chlamydial infections and prostatitis in men". BJU Int. 97 (4): 687–90. doi:10.1111/j.1464-410X.2006.06007.x. PMID 16536754. S2CID 34481915.
- ^ a b Lewis, Sharon Mantik (2017). Medical-surgical nursing : assessment and management of clinical problems. Bucher, Linda; Heitkemper, Margaret M. (Margaret McLean); Harding, Mariann (10th ed.). St. Louis, Missouri. ISBN 978-0-323-32852-4. OCLC 944472408.
- ^ Thylefors B, Négrel AD, Pararajasegaram R, Dadzie KY (1995). "Global data on blindness" (PDF). Bull World Health Organ. 73 (1): 115–21. PMC 2486591. PMID 7704921. Archived from the original (PDF) on 2008-06-25.
- ^ Resnikoff S, Pascolini D, Etya'ale D, Kocur I, Pararajasegaram R, Pokharel GP, Mariotti SP (2004). "Global data on visual impairment in the year 2002". Bull World Health Organ. 82 (11): 844–851. hdl:10665/269277. PMC 2623053. PMID 15640920.
- ^ Mabey DC, Solomon AW, Foster A (2003). "Trachoma". Lancet. 362 (9379): 223–9. doi:10.1016/S0140-6736(03)13914-1. PMID 12885486. S2CID 208789262.
- ^ World Health Organization. Trachoma Archived 2012-10-21 at the Wayback Machine. Accessed March 17, 2008.
- ^ Ngondi J, Onsarigo A, Matthews F, Reacher M, Brayne C, Baba S, Solomon AW, Zingeser J, Emerson PM (2006). "Effect of 3 years of SAFE (surgery, antibiotics, facial cleanliness, and environmental change) strategy for trachoma control in southern Sudan: a cross-sectional study". Lancet. 368 (9535): 589–95. doi:10.1016/S0140-6736(06)69202-7. PMID 16905023. S2CID 45018412.
- ^ a b c "STD Facts – Chlamydia". Center For Disease Control. December 16, 2014. Archived from the original on July 14, 2015. Retrieved 2015-07-24.
- ^ Williams D, Churchill D (2006). "Ulcerative proctitis in men who have sex with men: an emerging outbreak". BMJ. 332 (7533): 99–100. doi:10.1136/bmj.332.7533.99. PMC 1326936. PMID 16410585.
- ^ Gambhir, Manoj; Basáñez, María-Gloria; Turner, Felicity; Kumaresan, Jacob; Grassly, Nicholas C. (June 2007). "Trachoma: transmission, infection, and control". The Lancet. Infectious Diseases. 7 (6): 420–427. doi:10.1016/S1473-3099(07)70137-8. ISSN 1473-3099. PMID 17521595.
- ^ Leonhardt RM, Lee SJ, Kavathas PB, Cresswell P (2007). "Severe Tryptophan Starvation Blocks Onset of Conventional Persistence and Reduces Reactivation of Chlamydia trachomatis". Infect. Immun. 75 (11): 5105–17. doi:10.1128/IAI.00668-07. PMC 2168275. PMID 17724071.
- ^ Fairley CK, Gurrin L, Walker J, Hocking JS (2007). ""Doctor, How Long Has My Chlamydia Been There?" Answer:"... Years"". Sexually Transmitted Diseases. 34 (9): 727–8. doi:10.1097/OLQ.0b013e31812dfb6e. PMID 17717486.
- ^ Mpiga P, Ravaoarinoro M (2006). "Chlamydia trachomatis persistence: an update". Microbiol. Res. 161 (1): 9–19. doi:10.1016/j.micres.2005.04.004. PMID 16338585.
- ^ Bayramova, Firuza; Jacquier, Nicolas; Greub, Gilbert (2018). "Insight in the biology of Chlamydia-related bacteria". Microbes and Infection. Elsevier. 20 (7–8): 432–440. doi:10.1016/j.micinf.2017.11.008. PMID 29269129.
- ^ Klöckner, Anna; Bühl, Henrike; Viollier, Patrick; Henrichfreise, Beate (2018). "Deconstructing the Chlamydial Cell Wall". In Häcker, Georg (ed.). Biology of Chlamydia. Current Topics in Microbiology and Immunology. Vol. 412. Cham: Springer International Publishing. pp. 1–33. doi:10.1007/82_2016_34. ISBN 978-3-319-71232-1. PMID 27726004.
- ^ Gaydos CA; et al. (2004). "Comparison of three nucleic acid amplification tests for detection of Chlamydia trachomatis in urine specimens". J Clin Microbiol. 42 (7): 3041–3045. CiteSeerX 10.1.1.335.7713. doi:10.1128/JCM.42.7.3041-3045.2004. PMC 446239. PMID 15243057.
- ^ a b Haugland S, Thune T, Fosse B, Wentzel-Larsen T, Hjelmevoll SO, Myrmel H (2010). "Comparing urine samples and cervical swabs for Chlamydia testing in a female population by means of Strand Displacement Assay (SDA)". BMC Women's Health. 10 (1): 9. doi:10.1186/1472-6874-10-9. PMC 2861009. PMID 20338058.
- ^ "Recommendations for the Laboratory-Based Detection of Chlamydia trachomatis and Neisseria gonorrhoeae — 2014". www.cdc.gov. Archived from the original on 2016-06-27. Retrieved 2016-06-12.
- ^ Grillo-Ardila, CF; Torres, M; Gaitán, HG (29 January 2020). "Rapid point of care test for detecting urogenital Chlamydia trachomatis infection in nonpregnant women and men at reproductive age". The Cochrane Database of Systematic Reviews. 1: CD011708. doi:10.1002/14651858.CD011708.pub2. PMC 6988850. PMID 31995238.
- ^ Low, N; Redmond, S; Uusküla, A; van Bergen, J; Ward, H; Andersen, B; Götz, H (13 September 2016). "Screening for genital chlamydia infection". The Cochrane Database of Systematic Reviews. 2016 (9): CD010866. doi:10.1002/14651858.CD010866.pub2. PMC 6457643. PMID 27623210.
- ^ "National Chlamydia Screening Programme Data tables". www.chlamydiascreening.nhs.uk. Archived from the original on 2009-05-04. Retrieved 2009-08-28.
- ^ Desai, Monica; Woodhall, Sarah C; Nardone, Anthony; Burns, Fiona; Mercey, Danielle; Gilson, Richard (2015). "Active recall to increase HIV and STI testing: a systematic review". Sexually Transmitted Infections. 91 (5): sextrans–2014–051930. doi:10.1136/sextrans-2014-051930. ISSN 1368-4973. PMID 25759476Strategies for improved follow up care include the use of text messages and emails from those who provided treatment.
{{cite journal}}: CS1 maint: postscript (link) - ^ Eliopoulos GM, Gilbert DN, Moellering RC, eds. (2015). The Sanford guide to antimicrobial therapy 2011. Sperryville, VA: Antimicrobial Therapy, Inc. pp. 20. ISBN 978-1-930808-65-2.
- ^ Páez-Canro, C; Alzate, JP; González, LM; Rubio-Romero, JA; Lethaby, A; Gaitán, HG (25 January 2019). "Antibiotics for treating urogenital Chlamydia trachomatis infection in men and non-pregnant women". The Cochrane Database of Systematic Reviews. 1 (3): CD010871. doi:10.1002/14651858.CD010871.pub2. PMC 6353232. PMID 30682211.
- ^ Miller, Karl E. (2006-04-15). "Diagnosis and Treatment of Chlamydia trachomatis Infection". American Family Physician. 73 (8): 1411–1416. PMID 16669564. Archived from the original on November 27, 2011. Retrieved 2010-10-30.
- ^ Expedited Partner Therapy in the Management of Sexually Transmitted Diseases (2 February 2006) Archived 29 July 2017 at the Wayback Machine U.S. Department of Health and Human Services Public Health Service. Centers for Disease Control and Prevention National Center for HIV, STD, and TB Prevention
- ^ "WHO Disease and injury country estimates". World Health Organization. 2004. Archived from the original on 2009-11-11. Retrieved Nov 11, 2009.
- ^ Vos T, Flaxman AD, Naghavi M, Lozano R, Michaud C, Ezzati M, Shibuya K, Salomon JA, Abdalla S, et al. (Dec 15, 2012). "Years lived with disability (YLDs) for 1160 sequelae of 289 diseases and injuries 1990–2010: a systematic analysis for the Global Burden of Disease Study 2010". Lancet. 380 (9859): 2163–96. doi:10.1016/S0140-6736(12)61729-2. PMC 6350784. PMID 23245607.
- ^ a b "Detailed STD Facts – Chlamydia". www.cdc.gov. 20 September 2017. Retrieved 14 January 2018.
- ^ Torrone, E; Papp, J; Weinstock, H (Sep 26, 2014). "Prevalence of Chlamydia trachomatis Genital Infection Among Persons Aged 14–39 Years – United States, 2007–2012". MMWR. Morbidity and Mortality Weekly Report. 63 (38): 834–838. PMC 4584673. PMID 25254560.
- ^ "Chlamydia". UK Health Protection Agency. Archived from the original on 13 September 2012. Retrieved 31 August 2012.
External links
- Chlamydia at Curlie
- Chlamydia Fact Sheet from the CDC
| Classification | D
|
|---|---|
| External resources |
|
Sexually transmitted infections (STI) | |
|---|---|
| Bacterial |
|
| Protozoal |
|
| Parasitic |
|
| Viral |
|
| General inflammation |
|
Bacterial skin disease | |||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Gram +ve |
| ||||||||||||||||||
| Gram -ve |
| ||||||||||||||||||
| Unspecified pathogen |
| ||||||||||||||||||
UpToDate Contents
全文を閲覧するには購読必要です。 To read the full text you will need to subscribe.
- 1. クラミジア・トラコマチス感染の治療 treatment of chlamydia trachomatis infection
- 2. クラミジア・トラコマティス感染症の臨床症状および診断 clinical manifestations and diagnosis of chlamydia trachomatis infections
- 3. クラミジア・トラコマティス感染症の疫学 epidemiology of chlamydia trachomatis infections
- 4. 新生児におけるChlamydia trachomatis感染症 chlamydia trachomatis infections in the newborn
- 5. リンパ肉芽腫性病 lymphogranuloma venereum
English Journal
- The ΦCPG1 chlamydiaphage can infect Chlamydia trachomatis and significantly reduce its infectivity.
- Wei S, Liu Q, Lian T, Shao L.
- Virus research. 2019 Jul;267()1-8.
- Recent years have seen a significant increase in rates of persistent, antibiotic-resistant infection of Chlamydia trachomatis (CT) infections, representing an increasingly serious public health threat. At present there are no effective vaccines or antibodies available to treat CT, prompting the need
- PMID 31029735
- The possible role of bacteria, viruses, and parasites in initiation and exacerbation of irritable bowel syndrome.
- Shariati A, Fallah F, Pormohammad A, Taghipour A, Safari H, Chirani AS, Sabour S, Alizadeh-Sani M, Azimi T.
- Journal of cellular physiology. 2019 Jun;234(6)8550-8569.
- Irritable bowel syndrome (IBS) is a prolonged and disabling functional gastrointestinal disorder with the incidence rate of 18% in the world. IBS could seriously affect lifetime of patients and cause high economic burden on the community. The pathophysiology of the IBS is hardly understood, whereas
- PMID 30480810
- Targeted point-of-care testing compared with syndromic management of urogenital infections in women (WISH): a cross-sectional screening and diagnostic accuracy study.
- Verwijs MC, Agaba SK, Sumanyi JC, Umulisa MM, Mwambarangwe L, Musengamana V, Uwineza M, Cuylaerts V, Crucitti T, Jespers V, van de Wijgert JHHM.
- The Lancet. Infectious diseases. 2019 Jun;19(6)658-669.
- Sexually transmitted and urogenital infections are typically managed by WHO-recommended syndromic algorithms in resource-poor countries, and presumptively in Europe. However, algorithms for vaginal discharge and lower abdominal pain perform poorly in women. The women's improvement of sexual and repr
- PMID 31031172
Japanese Journal
- Cutaneous Vasculitis in Cogan's Syndrome: A Report of Two Cases Associated with Chlamydia Infection
- 日本医科大学雑誌 85(3), 172-177, 2018
- NAID 130007437638
- Prevalence and Genotype Distribution of <i>Chlamydia trachomatis</i> in Urine among Men Attending Sexually Transmitted Disease Clinics in Guangdong Province, China, in 2016
- Japanese Journal of Infectious Diseases 71(2), 104-108, 2018
- NAID 130006517103
Related Links
- Chlamydia trachomatis infection most commonly affects the urogenital tract. In men, the infection usually is symptomatic, with dysuria and a discharge from the penis. Untreated chlamydial infection in men can spread to ...
- I'm pregnant. How does chlamydia affect my baby? If you are pregnant and have chlamydia, you can pass the infection to your baby during delivery. This could cause an eye infection or pneumonia in your newborn. Having chlamydia ...
★リンクテーブル★
| リンク元 | 「クラミジアトラコマティス症」 |
| 関連記事 | 「Chlamydia trachomatis」「infection」「trachomatis」 |
「クラミジアトラコマティス症」
- 英
- Chlamydia trachomatis disease, Chlamydia trachomatis infection
- 同
- 性器クラミジア感染症 genital chlamydiosis
- 関
- Chlamydia trachomatis, STD、クラミジア感染症
治療
「Chlamydia trachomatis」
特徴
- 扁性細胞寄生菌 ← 細胞内への移行性・ペプチドグリカン無く、βラクタム無効、アミノグリコシド無効
- 細胞壁有り
- ペプチドグリカン無し
感染症
眼科
- SOP.176
- 新生児封入体結膜炎:母体が本菌による性器クラミジア感染症を発症しており、かつ経腟分娩で出生したときに新生児に見られる封入体結膜炎。
- 成人型封入体結膜炎:トラコーマとよばれている封入体結膜炎である。結膜と角膜を冒す。
産婦人科
- G9M.67,68,74
- 潜伏期間2-3週間で、多くは無症状で経過。帯下は軽度増量し、水様透明の漿液性
泌尿器科
- 尿道炎
- 精巣上体炎
一般的な治療
- マクロライド系抗菌薬(妊婦には特に)、キノロン系抗菌薬、テトラサイクリン系抗菌薬
国試
「infection」
- n.